One of the conditions in modern societies that often contributes to stress and anxieties is feeling insecure, threatened, or unsafe. There are many other factors to stress, anxiety and emotional disturbances. But, I want to address issues close to my heart; intrapsychic safety and security. I want to specifically address feeling unsafe and insecure.
Feeling unsafe intrapsychically will inevitably convert to maladaptive behaviours and compulsivity. Feeling insecure intrapsychically often lead to a lack of confidence in one’s own abilities and skills and distrustful of others, and the world.
 Generally, feelings are my friend, and I have made acquaintances with almost all of my emotions. I had come to accept feelings and emotions as a part of my experiences to be felt. I had embraced and incorporated feelings and emotions within my being. I have also allowed myself to mindfully and consciously express the feeling felt. I had even released inherited, trapped and preconception emotions, as well as unblocking heart-wall emotions. I had healed compound and post-traumatic emotional reverberation too. But, as an empath, I had learned the hard way how my feelings can still affect me, and most importantly, how other people’s emotions also impacted me. I had occasionally absorbed other people’s emotional resonances, and I had allowed that to affect me.
Generally, feelings are my friend, and I have made acquaintances with almost all of my emotions. I had come to accept feelings and emotions as a part of my experiences to be felt. I had embraced and incorporated feelings and emotions within my being. I have also allowed myself to mindfully and consciously express the feeling felt. I had even released inherited, trapped and preconception emotions, as well as unblocking heart-wall emotions. I had healed compound and post-traumatic emotional reverberation too. But, as an empath, I had learned the hard way how my feelings can still affect me, and most importantly, how other people’s emotions also impacted me. I had occasionally absorbed other people’s emotional resonances, and I had allowed that to affect me.
 Feeling unsafe and insecure are intrapsychic emotions. They are the core woundings from a less than ideal early environment in childhood. But, we do not have to let the past define the present or the future. These feelings often stemmed from inconsistency, chaotic and dismissive attachment patterns from our caregivers. But, they are not to blame because they too were the victim of their core woundings.
Feeling unsafe and insecure are intrapsychic emotions. They are the core woundings from a less than ideal early environment in childhood. But, we do not have to let the past define the present or the future. These feelings often stemmed from inconsistency, chaotic and dismissive attachment patterns from our caregivers. But, they are not to blame because they too were the victim of their core woundings.
Feeling unsafe arises when our external environment was hostile and threatening. A child may feel unsafe when their sense of self is physically or emotionally threatened. A child will also feel unsafe, lonely and abandoned when the caregiver is absent or when she is left alone for an extended period. If there is no one to mirror our being, we can lose sight of our beingness. The experiences can trigger body-memory retention, and their physiological response is usually a hypersensitivity to threats in the exterior world. Their fight/flight/freeze response is constantly on the alert and they are hypervigilant to fearful arousal. Imagine the toll this has on the body when it is permanently on alert.
 Feeling insecure, succeed feeling unsafe. When feeling insecure, a child feels awkward and inadequate in their abilities, skills and resources. The child lacks confidence, have doubts and distrusts themself, others and the world. Thus, the child will grow up to seek validation from the exterior world, thinking it would soothe their inner sanctum. When we are insecure about ourselves, we compensate for the lacking by constantly looking for ways to feel safe and secure. We also compensate by avoiding situations or people, and we may become controlling, adopting perfectionistic traits, or have obsessive-compulsive behaviours. We will often look for what is missing within outside of ourselves. We do this by collecting (material) things, including having people around us that makes us feel good. Unfortunately, we will not fully soothe that void looking externally when our intrapsychic world is unsafe.
Feeling insecure, succeed feeling unsafe. When feeling insecure, a child feels awkward and inadequate in their abilities, skills and resources. The child lacks confidence, have doubts and distrusts themself, others and the world. Thus, the child will grow up to seek validation from the exterior world, thinking it would soothe their inner sanctum. When we are insecure about ourselves, we compensate for the lacking by constantly looking for ways to feel safe and secure. We also compensate by avoiding situations or people, and we may become controlling, adopting perfectionistic traits, or have obsessive-compulsive behaviours. We will often look for what is missing within outside of ourselves. We do this by collecting (material) things, including having people around us that makes us feel good. Unfortunately, we will not fully soothe that void looking externally when our intrapsychic world is unsafe.
When I feel unsafe going someplace new, I used to make sure that I was early to the event. I would make sure that I arrived at least half an hour before the meeting to have time to settle down and relaxed. This behaviour allows me to feel like I was in control and it was a way of alleviating the discomfort, rather than looking at what was the cause. My strategy was to find ways to have control of situations or events. It was a strategy that worked for a time. Eventually, I had to look within to self-soothe.
In the perpetual cycle of self-fulling prophecy, a person seeks ways to feel safe and secure when feeling unsafe and insecure. However, you can find a way to self-soothe and settle the insecurity within the psyche. Here’s the good news. There are ways in which you can help yourself.
Here are some of the tools and techniques to help you build confidence, esteem and worth. They worked for me and I hope that they work for you too.
- Make time for Self-care
 Always put yourself first, you matter the most! This is not a selfish thought, but rather a self-care process. You have to look after number one (YOU). You have to move past caring for others first. Undoubtedly, we were conditioned to be considered, to be nice, to be kind to others. We were told to think of others, to be helpful and to be thoughtful of others. We were taught to believe that it matters what others think about us. But, in so doing, we neglected our own needs and care. I certainly thought that if I was helpful, nice and kind, somehow, I would feel safe in being altruistic.
Always put yourself first, you matter the most! This is not a selfish thought, but rather a self-care process. You have to look after number one (YOU). You have to move past caring for others first. Undoubtedly, we were conditioned to be considered, to be nice, to be kind to others. We were told to think of others, to be helpful and to be thoughtful of others. We were taught to believe that it matters what others think about us. But, in so doing, we neglected our own needs and care. I certainly thought that if I was helpful, nice and kind, somehow, I would feel safe in being altruistic.
However, it is more important that you treat yourself kindly through self-care rituals than being concerned with other’s people opinions. Self-care ritual is not simply just taking care of yourself physically, but also mentally too. Self-care mental constructs include positive words of affirmation for yourself, have compassion for mistakes of past events, and forgive yourself. For example, I have positive confirmations post-it notes all around the house to remind me of the positive qualities such as “I am safe!”, “I am comfortable in my skin!” etc.
- Stop making excuses and start doing
 When our external world is unsafe, we introspect and come to believe that our inner world is too. As we continue to think this way, we start to look for ways to feel safe and be safe. We tend to see threats when there are none. We make excuses for people, things and situations to minimise the threat, which may be imaginary. We may make excuses to change our behaviours and our mindsets because we are complacent in the familiar. This can keep us stuck in hypervigilant behaviours.
When our external world is unsafe, we introspect and come to believe that our inner world is too. As we continue to think this way, we start to look for ways to feel safe and be safe. We tend to see threats when there are none. We make excuses for people, things and situations to minimise the threat, which may be imaginary. We may make excuses to change our behaviours and our mindsets because we are complacent in the familiar. This can keep us stuck in hypervigilant behaviours.
Change is inevitable and we should embrace it. If you have a resistance to change, start with something small. Perhaps begin with a small change of routine, such as change the direction to work. Walk on a different side of the road! When we start to take these small steps to change it gets easier.
- Reframe the way you think
 What we think, we will manifest because it was impressed in the mind. If you think that you are not safe, lacking in confidence or not worthy you are essentially broadcasting this unconsciously. We don’t consciously mean to send out these unconscious perceptions but we do, and we project it.
What we think, we will manifest because it was impressed in the mind. If you think that you are not safe, lacking in confidence or not worthy you are essentially broadcasting this unconsciously. We don’t consciously mean to send out these unconscious perceptions but we do, and we project it.
Have you ever experience discomfort or uneasiness in a situation with someone and you don’t know why? It is possible that that person had unconsciously broadcast messages to your unconsciousness. You cannot see it but it is there. Just like the radiowaves being broadcasted from a radio station, you cannot see the radio wave but it is there nonetheless.
Reframing your thinking style simply means reverting the way you think. If you tend to be pessimistic, revert this to be optimistic. It is simply about changing your automatic thoughts and make them conscious. You will need to watch what you think to reframe your thoughts. If you often find yourself saying that you cannot do something, change this to you can! It is about fake it until you make it.
- Remind yourself that you are loved
 When we feel unsafe, threatened or insecure it is often because the love is not there. Our feelings begin internally as a result of an external stimulus that we introject, but we could also be absorbing other’s people energy and emotion, unconsciously. We can protect ourselves and keep safe by reminding ourselves that we are loved. We are loved by God. We are loved by the Higher Power. We are loved and we can draw power from the universe to recharge our battery, just as we recharge our body through grounding.
When we feel unsafe, threatened or insecure it is often because the love is not there. Our feelings begin internally as a result of an external stimulus that we introject, but we could also be absorbing other’s people energy and emotion, unconsciously. We can protect ourselves and keep safe by reminding ourselves that we are loved. We are loved by God. We are loved by the Higher Power. We are loved and we can draw power from the universe to recharge our battery, just as we recharge our body through grounding.
We simply need to visualise ourselves being loved, imagine feeling loved, feeling protected and feeling safe within the loving embrace. Try it, find a quiet place, be still and silent. Close your eyes and imagine feeling loved. Even if you have not experienced love in your reality, you can still imagine what it would be like to have loving feelings for yourself. It might help to think about what you love, to experience loving feelings.
I love my inner child! I imagine her face, the innocent, the bright eyes and I recalled other special features to help me feel that love. It might help if you have a photo of the child that you were. Really see her/him. Feel the love for her/him. Take as long as you need. You will know the experience of love when tears well up in your eyes. It might take some practising especially if your experiences of love was absent or hostile or if you are not connected to the essence of your inner child.
Once you have experienced love for yourself, you can emit and project that love towards others. Then wait, watch and see that love returned to you. According to the Universal Law of Attraction, what we give out, we will attract.
With faith, hope and trust, you too can find your safety and security intrapsychically within your inner world. If you hold love and positive intention within your heart, you will receive what you give out.
Do you find this blog helpful? If you like this post, I love to hear from you on my Twitter Page.
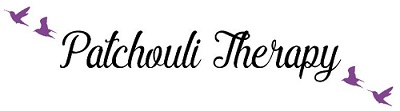




 Our physical body is made up of energy. Our emotions are energy. Everything is energy, and energy is everywhere. Emotions have energy. Our thoughts, whether it is conscious or unconscious, have an energy signature.
Our physical body is made up of energy. Our emotions are energy. Everything is energy, and energy is everywhere. Emotions have energy. Our thoughts, whether it is conscious or unconscious, have an energy signature.  However, energy can be explained by science. Energy is generated when there is an exertion of power or force, according to physicists. The quantitative law determines the exchanges of dynamic force in a reaction to cause and effect.
However, energy can be explained by science. Energy is generated when there is an exertion of power or force, according to physicists. The quantitative law determines the exchanges of dynamic force in a reaction to cause and effect. So, with summers coming, I want to share some of the ways you can protect your energy that has proven useful to me.
So, with summers coming, I want to share some of the ways you can protect your energy that has proven useful to me. It might be helpful if you can incorporate an energy cleansing activity into your daily ritual. You will find it easier to do and you won’t need to think of it as a chore if you build the activity in your life. You can begin to see subtle differences over time, or you might see a dramatic difference rightaway if your energy is stagnant.
It might be helpful if you can incorporate an energy cleansing activity into your daily ritual. You will find it easier to do and you won’t need to think of it as a chore if you build the activity in your life. You can begin to see subtle differences over time, or you might see a dramatic difference rightaway if your energy is stagnant.
 Acceptance is a concept of belief that recognises the validity of a thing or situation as it is. It is a conscious act with a positive intention for open-mindedness. It is to perceive something or a problem with a realistic view without judgement, assumption or supposition. In Psychology, acceptance is a catharsis, and it is a process of healing our cognition and emotion. But, if we can extend acceptance to all aspect of our lives and ourselves, we can come to a place of peace.
Acceptance is a concept of belief that recognises the validity of a thing or situation as it is. It is a conscious act with a positive intention for open-mindedness. It is to perceive something or a problem with a realistic view without judgement, assumption or supposition. In Psychology, acceptance is a catharsis, and it is a process of healing our cognition and emotion. But, if we can extend acceptance to all aspect of our lives and ourselves, we can come to a place of peace. To be able to accept what is, here are a few tips that I have tried and tested. They are the tools and strategies that work for me over the years in training and practising as a therapist. They may seem like common sense, but sometimes the simplest things are most effective.
To be able to accept what is, here are a few tips that I have tried and tested. They are the tools and strategies that work for me over the years in training and practising as a therapist. They may seem like common sense, but sometimes the simplest things are most effective. Accepting what is is a personal challenge that I sometimes struggle with because mistakes happen in the reality of a situation, especially in a relationship. It is an ongoing process, and one should not place emphasis on achieving and then forgetting it. It is not about ticking the box, and you are done with it. But, the more you practice and adopt this way of being, the more familiar you will become with accepting things, situation, people, life and yourself.
Accepting what is is a personal challenge that I sometimes struggle with because mistakes happen in the reality of a situation, especially in a relationship. It is an ongoing process, and one should not place emphasis on achieving and then forgetting it. It is not about ticking the box, and you are done with it. But, the more you practice and adopt this way of being, the more familiar you will become with accepting things, situation, people, life and yourself. Mental health has been a challenge that has recently spiked on the global scale since the pandemic. It has long been a part of Western societies since the birth of psychiatry, and possibly longer than that. Mental disturbances are a challenge that poses psychological and physical discomfort in the individual. Mental disturbances can range from worrying about your loved ones to concern for their safety and welfare. It is any disturbances that are constructed in the mind. The longer we are exposed to these disturbances, the more problem it poses on our mental health. Thus, our mental wellness depends on the way we think and how we construct our inner world.
Mental health has been a challenge that has recently spiked on the global scale since the pandemic. It has long been a part of Western societies since the birth of psychiatry, and possibly longer than that. Mental disturbances are a challenge that poses psychological and physical discomfort in the individual. Mental disturbances can range from worrying about your loved ones to concern for their safety and welfare. It is any disturbances that are constructed in the mind. The longer we are exposed to these disturbances, the more problem it poses on our mental health. Thus, our mental wellness depends on the way we think and how we construct our inner world. Mental health awareness is the ability to develop compassion for ourselves and our mental construct as well as the mental capability of another. It is also about treating ourselves and others the way we would like to be treated. It is about watching our thoughts and thinking well of ourselves and others. Having an awareness of our thought processes give us realisation. In the realisation, we become compassionate with ourselves and how our mind works things out.
Mental health awareness is the ability to develop compassion for ourselves and our mental construct as well as the mental capability of another. It is also about treating ourselves and others the way we would like to be treated. It is about watching our thoughts and thinking well of ourselves and others. Having an awareness of our thought processes give us realisation. In the realisation, we become compassionate with ourselves and how our mind works things out. You are more than your mind. Therefore, you are more than the way you think and what you think. Thinking is just what you happen to do because the brain does not shut up. Thoughts will always intrude on the psyche. But, thought forms, and then they disappear. When you give focus, attention and meaning to the ideas, your thinking and other thought-forms arise to become problematic. It is at this point that having a
You are more than your mind. Therefore, you are more than the way you think and what you think. Thinking is just what you happen to do because the brain does not shut up. Thoughts will always intrude on the psyche. But, thought forms, and then they disappear. When you give focus, attention and meaning to the ideas, your thinking and other thought-forms arise to become problematic. It is at this point that having a 
 A stressful situation for one person will inevitably be different. People are divergent and will have a different way to view or manage problems. From our lived experiences, these individuals can often draw upon their internal resources to cope with stress. However, it does not mean that you can’t learn to build your inner strength.
A stressful situation for one person will inevitably be different. People are divergent and will have a different way to view or manage problems. From our lived experiences, these individuals can often draw upon their internal resources to cope with stress. However, it does not mean that you can’t learn to build your inner strength. How we think and react can create or break the situation into a stressful or stress-free one. There are three main types of stress; acute, episodic and chronic. I shall now review the different kinds of stress in more details.
How we think and react can create or break the situation into a stressful or stress-free one. There are three main types of stress; acute, episodic and chronic. I shall now review the different kinds of stress in more details. Knowing what you think about will help you make sense of your inner voice. Listening to what you say and how you talk to yourself in a stressful situation will help you become in control of the situation, rather than allowing the problem to control you. We are often overly critical of ourselves. We can be the harshest critique. But, if we can be compassionate and kinder to ourselves, we can be free of the thoughts and let them go easier.
Knowing what you think about will help you make sense of your inner voice. Listening to what you say and how you talk to yourself in a stressful situation will help you become in control of the situation, rather than allowing the problem to control you. We are often overly critical of ourselves. We can be the harshest critique. But, if we can be compassionate and kinder to ourselves, we can be free of the thoughts and let them go easier. Now, try learning to speak to yourself differently. If you used to shout at yourself internally, why not try speaking softly this time. Hopefully, you will notice that the impact is dramatically reduced. You may start to notice an alternate feeling associated with the gentle inner voice. You also may hear yourself speaking using contrasting words, kinder and loving expression. The change begins with small and enlarges, like a ripple.
Now, try learning to speak to yourself differently. If you used to shout at yourself internally, why not try speaking softly this time. Hopefully, you will notice that the impact is dramatically reduced. You may start to notice an alternate feeling associated with the gentle inner voice. You also may hear yourself speaking using contrasting words, kinder and loving expression. The change begins with small and enlarges, like a ripple.




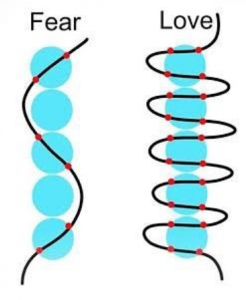 It often helps to name our emotions. This is because emotion has an
It often helps to name our emotions. This is because emotion has an 
 Qualities of compassion promote positive emotional response and mindset; however, it should not be compared to empathy. Compassion is a deep feeling for oneself and another person, whereas empathy is the ability to be alongside the other person, or in their shoes. The emotional response when perceiving suffering in oneself or another triggers an authentic desire and wishes to take action, to assist, to alleviate and to help – but not to eliminate or deny.
Qualities of compassion promote positive emotional response and mindset; however, it should not be compared to empathy. Compassion is a deep feeling for oneself and another person, whereas empathy is the ability to be alongside the other person, or in their shoes. The emotional response when perceiving suffering in oneself or another triggers an authentic desire and wishes to take action, to assist, to alleviate and to help – but not to eliminate or deny. I want to discuss the concept of masking in Psychology further.
I want to discuss the concept of masking in Psychology further. Fear not, I can offer some helpful tips to those individuals who’d like to remove their (psychological) masks – but keep the COVID-19 cover on (for now). Here’s how:
Fear not, I can offer some helpful tips to those individuals who’d like to remove their (psychological) masks – but keep the COVID-19 cover on (for now). Here’s how:
 Physiologically, people with strong ties or connections in a relationship have fewer health problems, less stressed, less depressed and improved mental wellness. Adverse to the effect, people who lack connection with themselves, others or their community have increased stress and depression, accelerated cardiovascular risks, loneliness, isolation and a higher chance of suicidal tendency.
Physiologically, people with strong ties or connections in a relationship have fewer health problems, less stressed, less depressed and improved mental wellness. Adverse to the effect, people who lack connection with themselves, others or their community have increased stress and depression, accelerated cardiovascular risks, loneliness, isolation and a higher chance of suicidal tendency.
 How well do you trust depends upon many factors. It is something that you learn, nurture and develop. It forms a set of behaviours and personality traits. It is also a belief with you hold as values and it determined your interaction with an individual. It is a sense of security within the relationship or process. It is dynamic and engaging. It is both benevolence and integral to all relationship within oneself, with others and with the world. If you have trust in yourself, in another and in the world, predictably, there will be cognizant.
How well do you trust depends upon many factors. It is something that you learn, nurture and develop. It forms a set of behaviours and personality traits. It is also a belief with you hold as values and it determined your interaction with an individual. It is a sense of security within the relationship or process. It is dynamic and engaging. It is both benevolence and integral to all relationship within oneself, with others and with the world. If you have trust in yourself, in another and in the world, predictably, there will be cognizant.